Eosinophilic Esophagitis

What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the esophagus—the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach. It happens when a type of white blood cell called eosinophils builds up in the lining of the esophagus, often due to an allergic reaction to certain foods or environmental allergens. This inflammation can cause symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, food getting stuck, chest pain, heartburn, and, in children, feeding difficulties or poor growth. EoE is diagnosed through endoscopy and biopsy, and treatment may include dietary changes to avoid trigger foods, medications to reduce inflammation, and managing underlying allergies to help keep symptoms under control.
What causes eosinophilic esophagitis?
Eosinophilic esophagitis develops when your immune system mounts an allergic response to a food or environmental substances such as pollen, mold, dust mites, and animal dander. The immune reaction triggers the accumulation of eosinophils in the esophagus. Repeated exposure to the irritant or allergen results in chronic inflammation and scarring. Though not as common, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) may cause or further aggravate eosinophilic esophagitis.
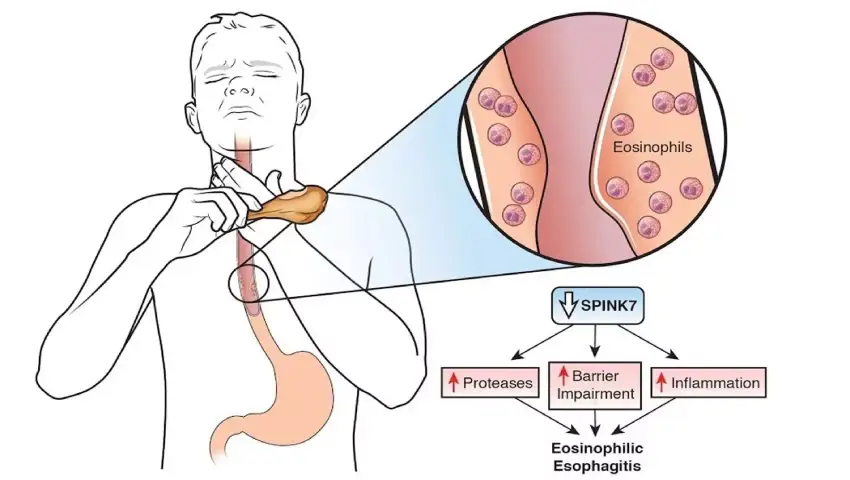
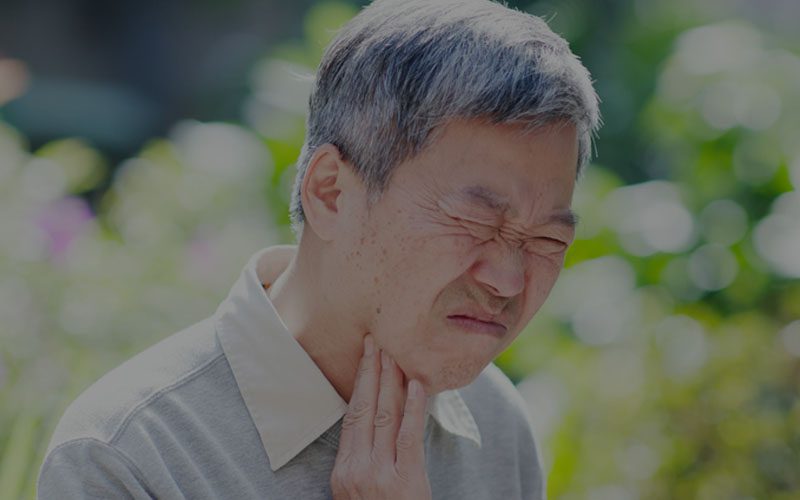
What symptoms develop due to eosinophilic esophagitis?
The esophagus narrows due to the inflammation and scar tissue, leading to symptoms such as:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Food stuck in the esophagus
- Chest pain that doesn’t respond to antacids
- Backflow of undigested food (regurgitation)
In addition to the above symptoms, children often experience nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and weight loss.
How do allergists diagnose eosinophilic esophagitis?
After reviewing your symptoms and completing a physical exam, your provider at Bellagio Family Medical, conducts allergy testing to identify your allergens. Your provider may also order blood tests or an endoscopy. During an endoscopy, they insert a narrow scope with a camera into your esophagus, allowing your provider to examine the esophageal lining.
How do allergists treat eosinophilic esophagitis?
Your treatment focuses on eliminating eosinophils, reducing the inflammation, and controlling your symptoms. Your personalized treatment plan may include:
Dietary changes
If you have a food allergy, eosinophilic esophagitis improves when you eliminate that food from your diet. Even if you don’t have a specific food allergy, your symptoms may improve with a special diet.
Medications
Taking a topical steroid reduces inflammation. This medication comes in the form of a liquid you swallow so that it comes into contact with esophageal tissues. If acid reflux contributes to the problem, a proton pump inhibitor may help.
Endoscopic treatment
In many cases, dietary changes and medications relieve your symptoms and restore normal function to the esophagus. If you have a severe esophageal narrowing or it stays constricted despite your treatment, your provider may perform an endoscopy to dilate the esophagus.
If you develop symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis, don’t wait to get help. Call or schedule an appointment online today.