Latex Allergy

What is Latex Allergy?
Latex allergy is an allergic reaction to natural rubber latex, a material commonly found in products like medical gloves, balloons, rubber bands, and some clothing or household items. It occurs when the immune system mistakes latex proteins for harmful substances and reacts against them. Symptoms can include skin redness, itching, hives, runny nose, sneezing, and itchy eyes. In severe cases, it can cause anaphylaxis—a life-threatening reaction with difficulty breathing and swelling of the throat. People with latex allergy should avoid latex-containing products and use safe alternatives, such as latex-free gloves and medical supplies.
What are the signs of a latex allergy?
A latex allergy can cause symptoms such as:
- Red skin
- Itchy skin
- Swollen skin
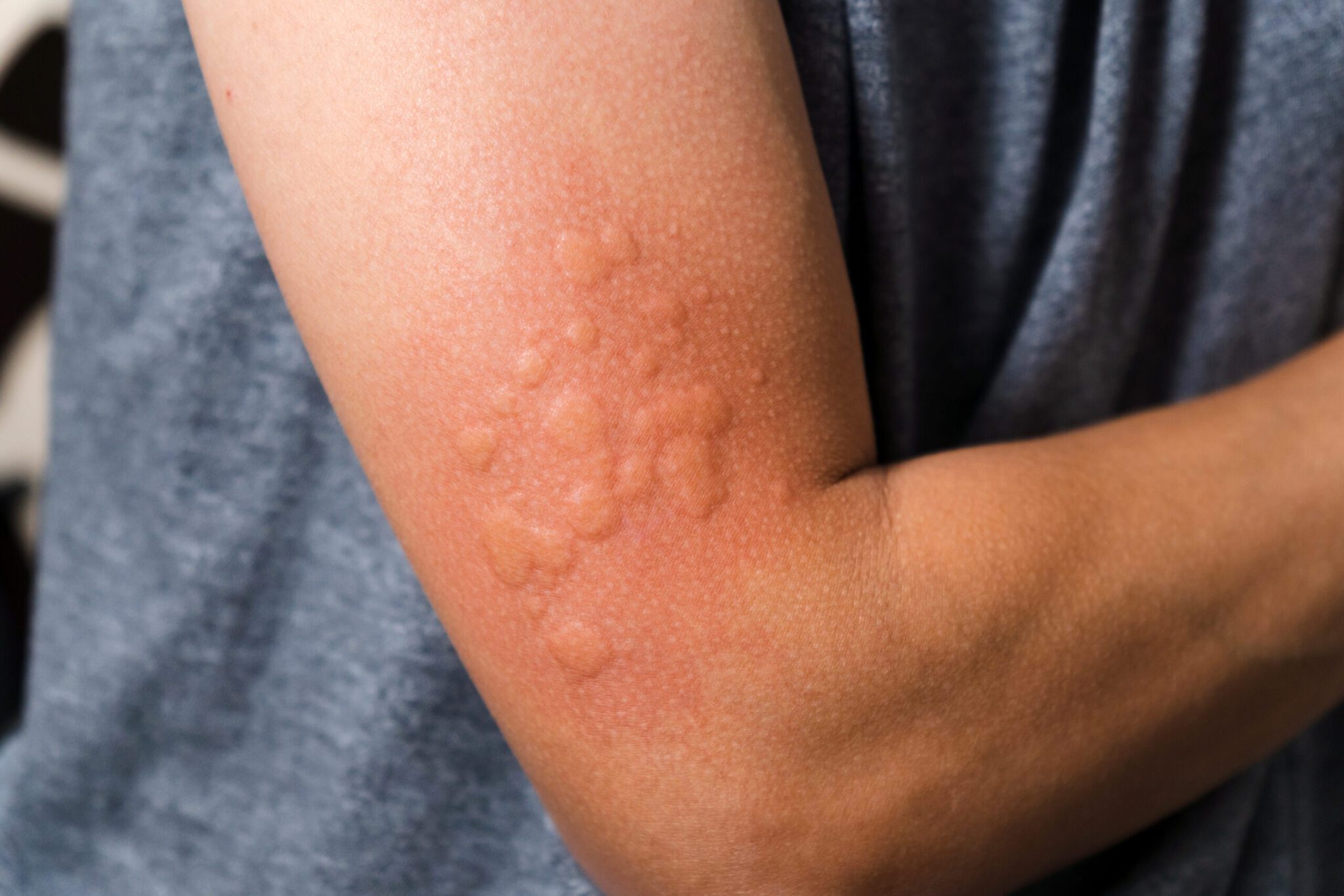
- Hives
- Nasal symptoms like runny nose or sneezing
- Red eyes
- Difficulty breathing
Latex allergies can potentially cause anaphylaxis, a severe whole-body reaction that may include rash, vomiting, breathing problems, chest pain, fainting, and shock. Anaphylaxis can be deadly, so fast reaction time is critical if you suspect a latex allergy.
More about latex allergy?
A latex allergy means that you’re allergic to a component of the sap from the Brazilian rubber tree or to one of the chemicals used in the creation of latex. Several commonly used products contain latex, including rubber bands, elastic bandages, rubber gloves, and balloons. Latex allergies can occur when you touch a latex-containing product or when inhaling microscopic latex particles.
Types of latex allergies include:
IgE-mediated
An IgE-mediated latex allergy is a protein allergy in which your immune system reacts severely to any latex exposure. This type of latex allergy can be life-threatening.
Cell-mediated contact dermatitis
Cell-mediated contact dermatitis is an allergic reaction to latex production chemicals. This latex allergy isn’t life-threatening, but it can cause uncomfortable skin reactions a day or two after exposure.
Irritant contact dermatitis
Technically, irritant contact dermatitis isn’t a latex allergy. It’s a reaction that features an itchy rash. It’s most common among health care workers who regularly wear latex gloves.Latex allergies can be quite serious, so it’s important to get diagnosis and treatment as soon as possible. Your body can shift from one type of latex allergy to another. For example, most IgE-mediated latex allergy sufferers had irritant contact dermatitis first.
How are latex allergies treated?
The best protection is knowing as much as possible about your specific type of allergy and then taking precautions recommended by your allergist. The Bellagio Family Medical, team helps with every aspect of latex allergies, including testing, diagnosis, education, and treatment. Although avoiding latex is essential, you may still have accidental exposure at times. Your doctor may prescribe corticosteroids or antihistamines for mild-to-moderate reactions. If you have life-threatening latex allergies, your doctor may prescribe injectable epinephrine to have with you at all times.
Don’t risk your life by ignoring latex reactions. The Bellagio Family Medical, team is here for you, so call the office nearest you or schedule an appointment online today.
Intradermal testing
Intradermal testing is like a skin prick test, except the allergen is injected under the surface of your skin. Your provider at Bellagio Family Medical, may do intradermal testing if your skin prick test was negative, and they want to verify the results.
Does allergy testing include a blood test?
Blood tests accurately identify your allergens, but your provider uses this type of allergy testing primarily for patients with a skin condition that prevents a skin test. They may also use blood tests to follow your food allergy or sensitivity over time.
When do I need a patch test?
Patch testing identifies common contact allergens such as poison ivy, detergents, nickel, and other metals. Your patch may contain a variety of the most common contact local allergens. The team at Bellagio Family Medical, can also customize your patch test and use specific products you bring from home that may cause your allergic reaction. After placing the allergens in isolated squares on a large, self-adhesive patch, your provider places the patch on your back. Since it takes time for this type of allergen to cause a reaction, you wear the patch for 48 hours. At the end of 48 hours, you go back to Bellagio Family Medical, and your provider checks the skin under the patch. If you don’t have any skin reactions, you may need to wear the patch for several more days.
If you’re ready to take control of your allergies, allergy testing is the first step. Call Bellagio Family Medical, or book an appointment online today.